Which diagram represents a perpendicular distance in Euclidean geometry? This question delves into the realm of geometry, where understanding perpendicular distance is crucial. Perpendicular distance, the shortest distance between a point and a line or plane, finds applications in architecture, engineering, and surveying, making it a fundamental concept in Euclidean geometry.
To delve deeper into this topic, we will explore the different types of diagrams that can represent perpendicular distance, including right triangles, perpendicular lines, and parallel lines. We will also provide steps on how to identify perpendicular distance in various types of diagrams and discuss its practical applications.
Definition of Perpendicular Distance in Euclidean Geometry

In Euclidean geometry, the perpendicular distance between two geometric objects is the shortest distance between them measured along a line perpendicular to both objects. It is also known as the normal distance or the shortest distance without overlap.
Examples of perpendicular distances in real-world scenarios include:
- The distance from a point to a line
- The distance between two parallel lines
- The height of a triangle
- The radius of a circle
Types of Diagrams Representing Perpendicular Distance
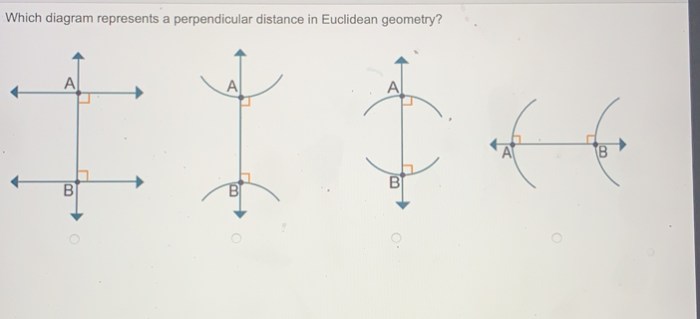
There are several types of diagrams that can represent perpendicular distance in Euclidean geometry, including:
- Right triangles:In a right triangle, the perpendicular distance between the hypotenuse and the opposite side is the height of the triangle.
- Perpendicular lines:Two lines are perpendicular if they intersect at a right angle. The perpendicular distance between two perpendicular lines is the distance between any point on one line and the other line.
- Parallel lines:Two lines are parallel if they never intersect. The perpendicular distance between two parallel lines is the distance between any point on one line and the other line.
Identifying Perpendicular Distance in Diagrams
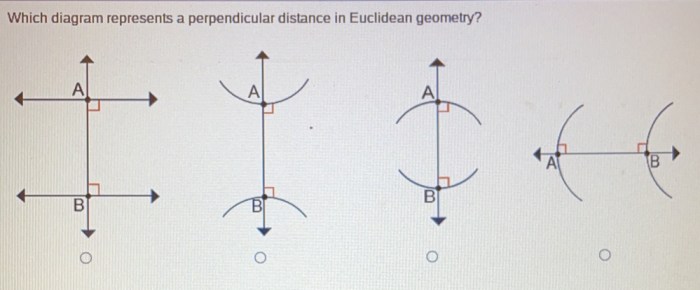
To identify the perpendicular distance in a diagram, follow these steps:
- Identify the two geometric objects between which you want to find the perpendicular distance.
- Draw a line perpendicular to both objects.
- Measure the distance along the perpendicular line from one object to the other.
Applications of Perpendicular Distance in Euclidean Geometry
Perpendicular distance has numerous practical applications in Euclidean geometry, including:
- Architecture:Determining the height of a building or the distance between two buildings.
- Engineering:Calculating the forces acting on a structure or the distance between two objects.
- Surveying:Measuring the distance between two points on the ground or the height of a mountain.
Examples and Illustrations
Example 1:Find the perpendicular distance from the point (3, 4) to the line y = 2x + 1.
Solution:The perpendicular distance from a point to a line is the shortest distance between the point and the line. To find the perpendicular distance, we need to find the equation of the line perpendicular to the given line and passing through the given point.
The slope of the given line is 2, so the slope of the perpendicular line is -1/2. The equation of the perpendicular line is y = (-1/2)x + b, where b is the y-intercept.
To find the y-intercept, we substitute the coordinates of the given point into the equation of the perpendicular line:
4 = (-1/2)(3) + b b = 7/2
Therefore, the equation of the perpendicular line is y = (-1/2)x + 7/2.
Now, we can find the perpendicular distance by finding the distance between the given point and the perpendicular line. The perpendicular distance is the length of the line segment from the given point to the perpendicular line. The length of this line segment is:
sqrt((3 - (-3/2))^2 + (4 - (7/2))^2) = sqrt(49/4 + 9/4) = sqrt(58/4) = sqrt(14.5) ≈ 3.81
Therefore, the perpendicular distance from the point (3, 4) to the line y = 2x + 1 is approximately 3.81 units.
Question Bank: Which Diagram Represents A Perpendicular Distance In Euclidean Geometry
What is perpendicular distance in Euclidean geometry?
Perpendicular distance is the shortest distance between a point and a line or plane.
How can we identify perpendicular distance in diagrams?
To identify perpendicular distance in diagrams, we can use geometric principles such as the Pythagorean theorem and the properties of perpendicular lines and parallel lines.
What are the applications of perpendicular distance in real-world scenarios?
Perpendicular distance has applications in architecture, engineering, and surveying, where it is used to determine distances, angles, and other geometric relationships.