Embark on a captivating journey through the Map of US Railroads in 1900, where the iron tracks tell a tale of rapid expansion, technological advancements, and profound societal impact. As we delve into this intricate network, we’ll explore the factors that fueled its growth, the key lines that crisscrossed the nation, and the transformative role it played in shaping the destiny of the United States.
From the bustling cities of the East to the untamed frontier of the West, railroads became the arteries of commerce and communication, connecting communities and driving economic prosperity. Their impact extended far beyond the tracks, influencing social and cultural landscapes, facilitating westward expansion, and fostering the growth of industries that would define the modern world.
Railroad Expansion in the United States
The late 19th century witnessed a surge in railroad expansion across the United States, transforming the nation’s transportation landscape and economy. This growth was driven by a confluence of factors, including the country’s vast landmass, the need for efficient transportation of goods and people, and government policies that incentivized railroad development.The
vastness of the United States presented a significant challenge for transportation. Before the advent of railroads, travel and commerce relied heavily on waterways and rudimentary roads, which were often slow, unreliable, and expensive. Railroads offered a more efficient and reliable means of transporting goods and people over long distances, enabling the rapid expansion of markets and the growth of industries.The
government played a crucial role in encouraging railroad development through its land grant policies. The Pacific Railway Act of 1862 granted vast tracts of land to railroad companies for each mile of track they built. These land grants provided a significant financial incentive for companies to invest in railroad construction, as they could sell the land to settlers and generate additional revenue.As
a result of these factors, the United States experienced a period of rapid railroad expansion during the late 19th century. Numerous railroad companies emerged during this period, including the Union Pacific Railroad, the Central Pacific Railroad, and the Southern Pacific Railroad.
These companies played a vital role in connecting the nation’s eastern and western regions, facilitating the growth of cities, industries, and agriculture.
Key Railroad Lines and Routes
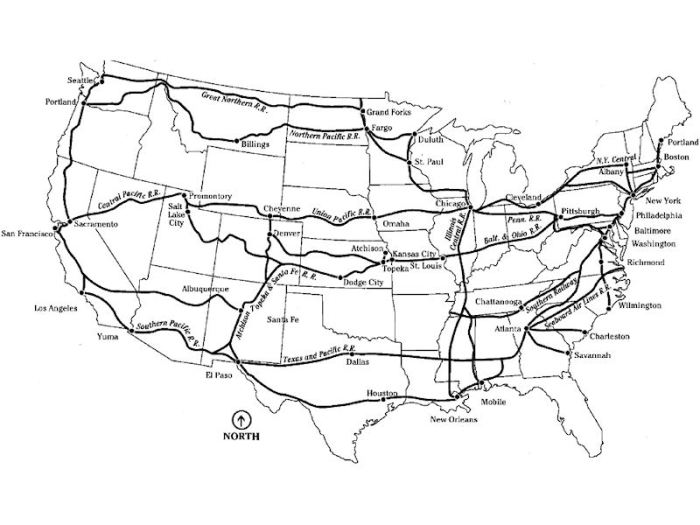
The rapid expansion of railroads in the United States during the late 19th century transformed the nation’s transportation system. By 1900, the country boasted an extensive network of railroad lines that crisscrossed the continent, connecting major cities, industrial centers, and agricultural regions.
These lines played a pivotal role in the economic development and westward expansion of the United States.
Major Railroad Lines
Some of the most important railroad lines that existed in the US in 1900 included:
- Transcontinental Railroad:Completed in 1869, this line connected the eastern and western United States, providing a vital link for the transportation of goods and people.
- Northern Pacific Railroad:This line ran from St. Paul, Minnesota, to Seattle, Washington, and was crucial for the development of the Pacific Northwest.
- Southern Pacific Railroad:This line connected New Orleans, Louisiana, to San Francisco, California, and played a key role in the growth of the American Southwest.
- Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway:This line ran from Chicago, Illinois, to Los Angeles, California, and was instrumental in the development of the American West.
These lines, along with numerous other regional and local railroads, formed an intricate network that facilitated the movement of goods and people across the country.
Social and Cultural Impacts: Map Of Us Railroads In 1900
Railroads had a profound impact on American society, facilitating the movement of people and ideas across the vast country. They played a crucial role in the growth of cities and towns along their routes, fostering economic development and cultural exchange.
Population Movement and Settlement
Railroads enabled the mass migration of people westward, opening up new territories for settlement and agriculture. They made it possible for individuals and families to relocate quickly and affordably, leading to the rapid expansion of the American frontier. The availability of transportation also encouraged immigration from Europe, as people sought opportunities in the United States.
Economic Development, Map of us railroads in 1900
Railroads stimulated economic growth by connecting producers with consumers over long distances. They transported raw materials to factories and finished goods to markets, facilitating the development of industries and businesses. The construction of railroads also created jobs and boosted local economies along their routes.
Cultural Exchange
Railroads facilitated the spread of ideas and culture across the country. They transported newspapers, books, and other printed materials, which helped to inform and educate the public. The movement of people also led to the exchange of cultural traditions and practices, contributing to the diversity and richness of American society.
Technological Advancements
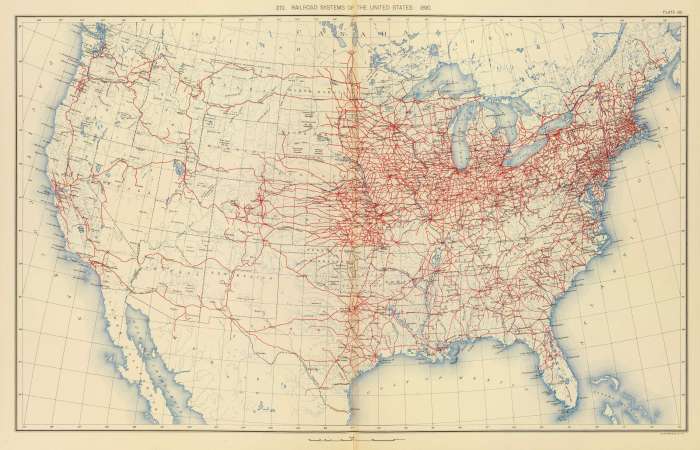
The late 19th century witnessed significant technological advancements that revolutionized the development and operations of railroads in the United States. These advancements played a crucial role in enhancing the efficiency, safety, and overall impact of railroads on the nation’s transportation infrastructure.
Steam Locomotives
The development of steam locomotives was a pivotal advancement that transformed railroad transportation. These locomotives, fueled by coal or wood, provided a reliable and efficient means of hauling heavy loads over long distances. The ability of steam locomotives to generate immense power and maintain consistent speeds greatly improved the speed and capacity of railroad operations.
Standardized Track Gauges
The standardization of track gauges emerged as another key factor in the expansion and efficiency of railroads. Prior to standardization, different railroad companies used varying track gauges, hindering the smooth transfer of rolling stock between lines. The adoption of a standardized gauge, initially 4 ft 8.5 in (1.435 m), allowed for seamless interoperability between different railroads, facilitating the movement of goods and passengers across the country.
The intricate network of railroads that crisscrossed the United States in 1900, as depicted on a detailed map, offers a glimpse into the nation’s industrial expansion. These iron arteries played a crucial role in transporting goods and people, fostering economic growth.
As we delve into the map, we stumble upon a curious rhythm, one that echoes the cadence of a marching navy: one by one , the trains chugged along the tracks, carrying the weight of a burgeoning nation’s hopes and dreams.
And as we trace their paths, we appreciate anew the vital role these railroads played in shaping the destiny of the United States.
Air Brakes
The invention and implementation of air brakes marked a significant safety advancement for railroads. Prior to their introduction, trains relied on hand brakes applied individually to each car, making it challenging to stop long trains effectively and safely. Air brakes, operated by a single engineer, provided a centralized and more efficient means of braking, greatly reducing stopping distances and enhancing overall safety.
Competition and Consolidation
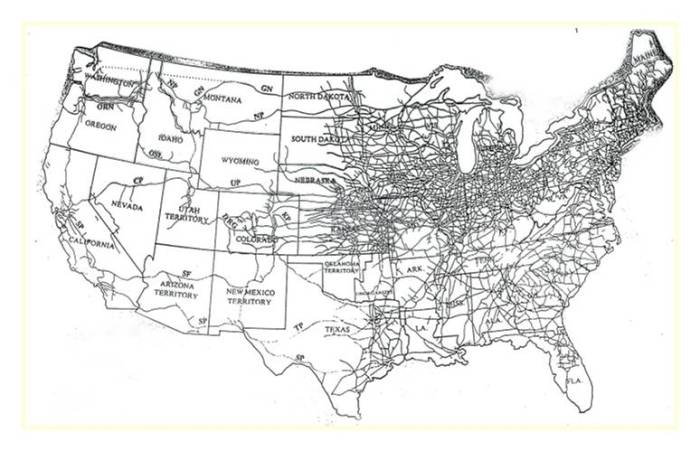
The late 19th century witnessed fierce competition among railroad companies in the United States. As the industry expanded rapidly, numerous companies emerged, each seeking to establish dominance in various regions.
To gain a competitive edge, railroad companies engaged in various strategies, including rate wars, which led to significant price fluctuations and financial instability. In an effort to stabilize the industry and increase efficiency, mergers and consolidations became prevalent.
Major Railroad Mergers
- Pennsylvania Railroad and New York Central Railroad (1899):This merger created one of the largest railroad systems in the country, connecting the East Coast with the Midwest.
- Northern Pacific Railroad and Great Northern Railway (1901):This merger formed the largest railroad system in the West, spanning from the Great Lakes to the Pacific Ocean.
- Southern Pacific Railroad and Union Pacific Railroad (1901):This merger created a transcontinental railroad system, connecting the West Coast with the East Coast.
Essential FAQs
What factors contributed to the rapid expansion of railroads in the US?
Government land grant policies, technological advancements, and the demand for efficient transportation.
How did railroads impact the US economy?
They facilitated industrial growth, westward expansion, and the development of new markets.
What were some of the major railroad companies that emerged during this period?
Union Pacific, Southern Pacific, and Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway.